Swollen Ear Here is Everything You Need to Know

Overview
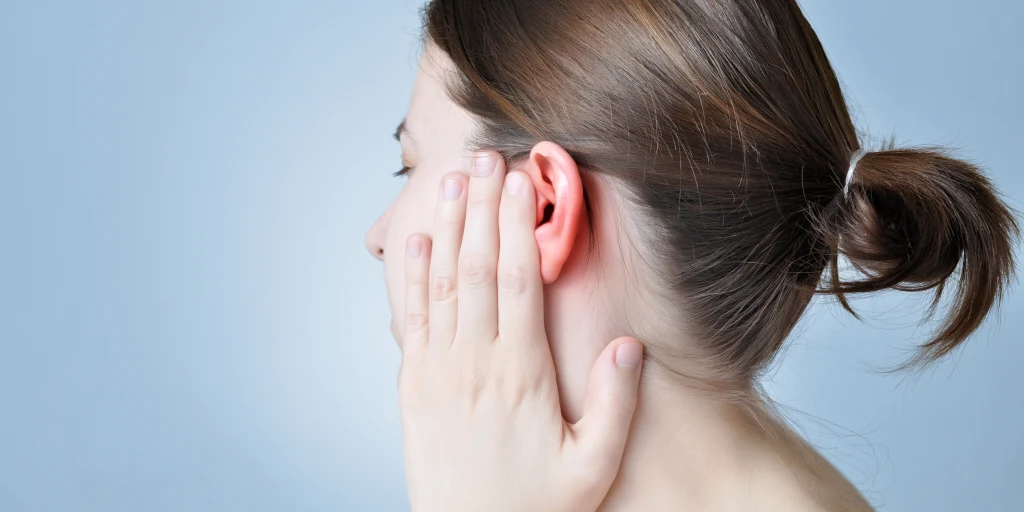
A swollen ear refers to inflammation or puffiness affecting the outer, middle, or inner ear. It often occurs due to infection, injury, allergic reactions, or fluid buildup. Swelling may cause pain, redness, itching, or temporary hearing discomfort, depending on the underlying cause.
1:What is swollen ear?
is a condition where part of the ear becomes enlarged, puffy, or inflamed. It can affect the outer ear, ear canal, or inner structures and is commonly caused by infection, injury, allergies, insect bites, or fluid buildup.
2:When and Why Ear Canal Swelling Happens?
A swollen ear occurs when the ear tissues react to irritation, infection, or injury. It can happen at any age and at any time. Common causes include bacterial or viral ear infections, allergies, insect bites, excessive ear cleaning, or wearing tight ear accessories. Swimming in contaminated water can also lead to ear canal infections that cause swelling. In some cases, ear swelling develops after trauma, such as a blow to the ear or prolonged pressure from headphones. Poor ear hygiene and untreated skin conditions may also increase the risk of developing ear swelling.
3:What Causes a Swollen Ear Canal?
An ear canal is a common ear problem that can affect people of all ages. The ear canal is the narrow passage that connects the outer ear to the eardrum, and when this area becomes inflamed or irritated, it can lead to pain, itching, redness, discharge, and sometimes hearing discomfort. Understanding the causes of an ear canal is important because early identification helps prevent complications and ensures proper treatment. Below are the most common and medically recognized causes of ear canal swelling, explained in detail.
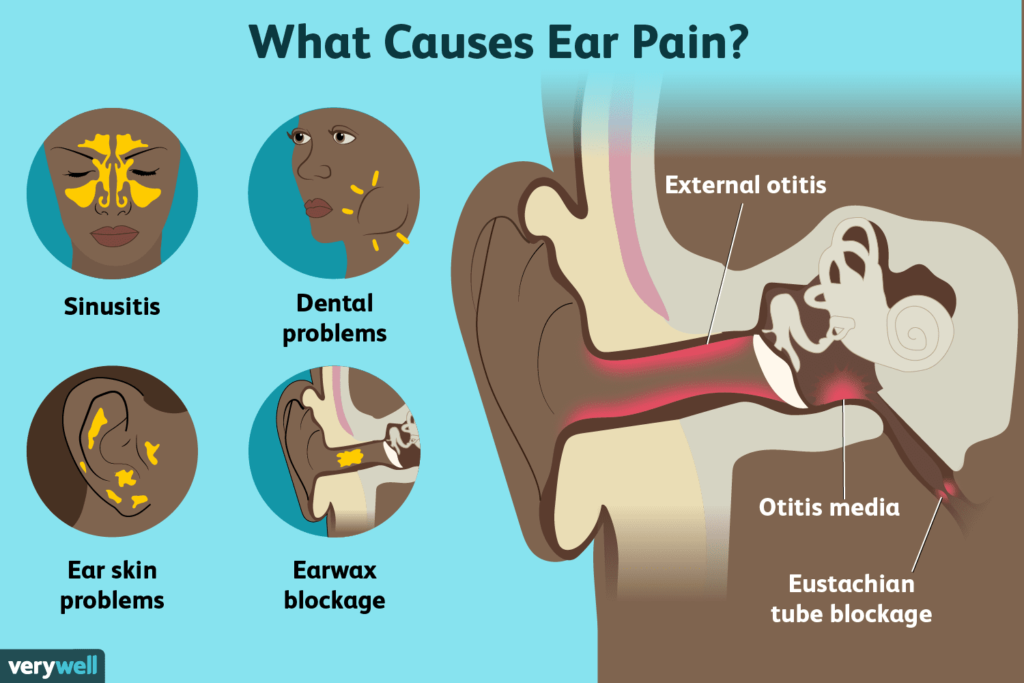
1. Ear Infections (Otitis Externa)
One of the most common causes of a ear canal is otitis externa, also known as swimmer’s ear. This condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect the skin of the ear canal. Moisture trapped in the ear after swimming or bathing creates an ideal environment for microorganisms to grow.Symptoms often include swelling, redness, itching, pain that worsens when touching the ear, and fluid discharge. If left untreated, the swelling can increase and partially block the ear canal, affecting hearing.
2. Excess Moisture in the Ear
Water that remains inside the ear canal for long periods can weaken the skin’s natural protective barrier. This makes the ear canal more vulnerable to irritation and infection. People who swim frequently, live in humid climates, or sweat excessively around the ears are at higher risk.Even daily activities such as showering without drying the ears properly can contribute to persistent moisture, leading to inflammation and swelling over time.
3. Allergic Reactions
Allergies can also cause a swollen ear canal. Reactions to hair products, shampoos, soaps, ear drops, or metals in earrings may irritate the sensitive skin inside the ear. In such cases, the swelling is usually accompanied by itching, redness, and dryness rather than severe pain.Contact dermatitis inside the ear canal can develop gradually and worsen if exposure to the allergen continues.
4. Excessive Ear Cleaning
Using cotton swabs, hairpins, or other objects to clean the ears is a common but harmful practice. These tools can scratch or damage the delicate skin of the ear canal, leading to inflammation and swelling.Over-cleaning can also remove natural earwax, which plays an important role in protecting the ear canal from bacteria and debris. Without this natural barrier, the ear becomes more prone to irritation and infection.
5. Earwax Buildup or Impacted Earwax
While earwax is protective, excessive buildup can cause problems. Impacted earwax can trap moisture, irritate the ear canal, and lead to swelling. In some cases, attempts to remove earwax at home push it deeper into the canal, worsening the condition.Swelling caused by earwax buildup may be accompanied by a feeling of fullness, muffled hearing, and discomfort.
6. Skin Conditions
Certain skin conditions can affect the ear canal and cause swelling. These include eczema, psoriasis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Such conditions make the skin dry, flaky, and prone to cracking, which increases the risk of inflammation and infection.People with chronic skin conditions often experience recurring ear canal swelling, especially during flare-ups.
7. Bacterial or Fungal Growth
The ear canal naturally contains microorganisms, but an imbalance can lead to infection. Bacterial infections are more common and usually cause pain and discharge, while fungal infections may cause intense itching and a feeling of fullness. Both types of infections can result in noticeable swelling of the ear canal and may require medical treatment to resolve completely.
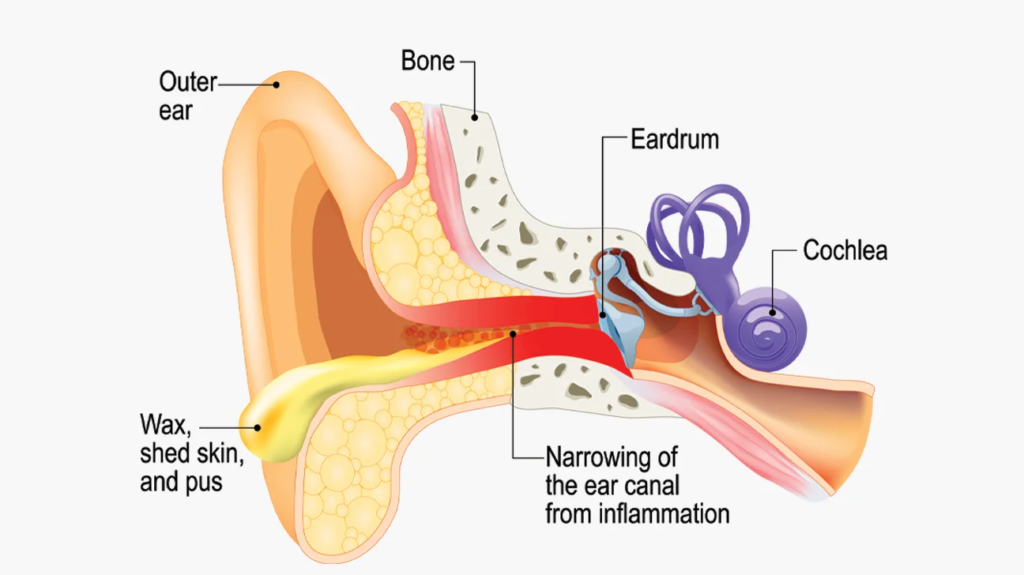
8. Injury or Trauma
Physical trauma to the ear canal can cause swelling. This may occur due to accidental injury, insertion of sharp objects, or irritation from hearing aids and earplugs that do not fit properly.Even minor injuries can trigger inflammation, especially if bacteria enter the damaged skin.
9. Use of Ear Devices
Prolonged use of earphones, earbuds, hearing aids, or earplugs can irritate the ear canal. Poorly cleaned devices may also introduce bacteria into the ear.Constant pressure and friction from these devices can cause swelling, especially when combined with heat and moisture.
10. Weakened Immune System
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or chronic illnesses, are more prone to ear canal infections and inflammation. Their bodies may have difficulty fighting off bacteria and fungi, making swelling more severe and longer lasting.In such cases, a swollen ear canal should be taken seriously and treated promptly.
11. Environmental Factors
Environmental irritants like dust, pollution, chemicals, or smoke can irritate the ear canal. Long-term exposure may lead to chronic inflammation and recurring swelling.People working in dusty or industrial environments are at greater risk if proper ear protection is not used.
12. Blocked Ear Canal Due to Foreign Objects
In children, small objects placed in the ear can block the canal and cause swelling. In adults, insects entering the ear or debris getting trapped can also lead to irritation and inflammation.A blocked ear canal often causes pain, swelling, and sudden hearing changes.
13. Spread of Nearby Infections
Infections from nearby areas, such as the outer ear or surrounding skin, can spread into the ear canal. This secondary involvement can cause swelling and discomfort, especially if treatment is delayed.
14. Poor Ear Hygiene
Neglecting ear hygiene can allow dirt, sweat, and bacteria to accumulate in the ear canal. While over-cleaning is harmful, complete neglect can also increase the risk of swelling and infection.Balanced ear care is essential to maintain ear health.
4:Can an ear canal heal itself?
Yes, an ear canal can heal on its own if the cause is mild, such as slight irritation, minor injury, or temporary moisture buildup. Keeping the ear clean and dry, avoiding ear picking or inserting objects, and limiting exposure to water can support natural healing. However, if swelling, pain, or discharge persists, medical treatment may be necessary.
5:How to bring down swelling in the ear canal?
To bring down swelling in the ear canal, keep the ear clean and dry and avoid inserting any objects into it. Applying a warm compress to the outer ear may help reduce discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relief can ease inflammation, while avoiding water exposure prevents irritation. If swelling continues or worsens, using prescribed ear drops and consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
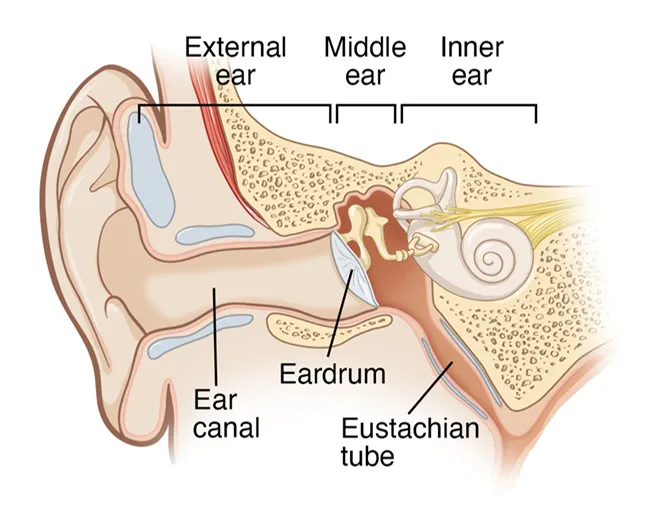
6:At home solutions not helping your ear canal?
If at-home solutions are not helping your ear canal, it may indicate an infection or more serious underlying issue. Persistent swelling, pain, or discharge should not be ignored. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. A doctor may prescribe antibiotic or antifungal ear drops, recommend cleaning the ear safely, or suggest other medical interventions to reduce inflammation and prevent complications, ensuring faster and safer recovery.
7:Changes in an Ear Canal
1:Blocked Ear Sensation
A swollen ear canal can cause several noticeable changes, both physically and in how you hear. Initially, the ear may appear red and slightly puffy due to inflammation. As swelling progresses, the ear canal may feel tight or blocked, leading to a sensation of fullness. You might also notice discomfort or pain, which can range from mild irritation to sharp, throbbing pain depending on the cause.
2:Sound Distortion
Hearing changes are common when the canal swells. Sound may become muffled, making it difficult to hear clearly. This occurs because the swelling partially blocks the passage of sound waves to the eardrum. In some cases, fluid buildup inside the canal can worsen the muffled hearing or create a sensation of pressure.
3:Itching and Irritation
Other changes may include itching, warmth, and sometimes a discharge if the swelling is due to infection. Skin around the ear canal may appear flaky or irritated, especially in allergic reactions or skin conditions like eczema.
4:Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
It is important to monitor these changes. If swelling persists, worsens, or is accompanied by severe pain, fever, or discharge, medical attention is necessary. Timely intervention can prevent complications, restore hearing, and reduce discomfort, ensuring the ear canal returns to its normal, healthy state.
8:Symptoms of a Swollen Ear Canal
A ear canal can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on the cause. Common signs include redness, puffiness, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Pain or discomfort, ranging from mild irritation to sharp or throbbing pain, is often present. Itching and warmth may accompany the swelling, especially in allergic reactions or infections. Hearing may become muffled or temporarily reduced due to partial blockage of the canal. In some cases, fluid discharge, foul odor, or crusting may occur if an infection is involved. Early recognition of these symptoms is essential for effective treatment.
9:Medical Treatments
When at-home remedies fail or the swelling is severe, medical treatments are often necessary. Doctors first examine the ear to determine the cause, such as bacterial or fungal infection, injury, or allergic reaction.
1:Reducing Inflammation
For bacterial infections, antibiotic ear drops or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce infection and inflammation. Fungal infections are treated with antifungal ear drops specifically designed to eliminate fungal growth in the canal. Pain and swelling can be managed with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers.
2:Professional Ear Cleaning
In cases where swelling is caused by impacted earwax or foreign objects, a healthcare professional may perform ear canal cleaning or removal procedures using safe medical techniques. Severe or chronic cases may require corticosteroid drops to reduce inflammation and speed healing.It is crucial to follow medical advice carefully and avoid inserting objects into the ear, as improper handling can worsen swelling or cause permanent damage to the ear canal and eardrum.
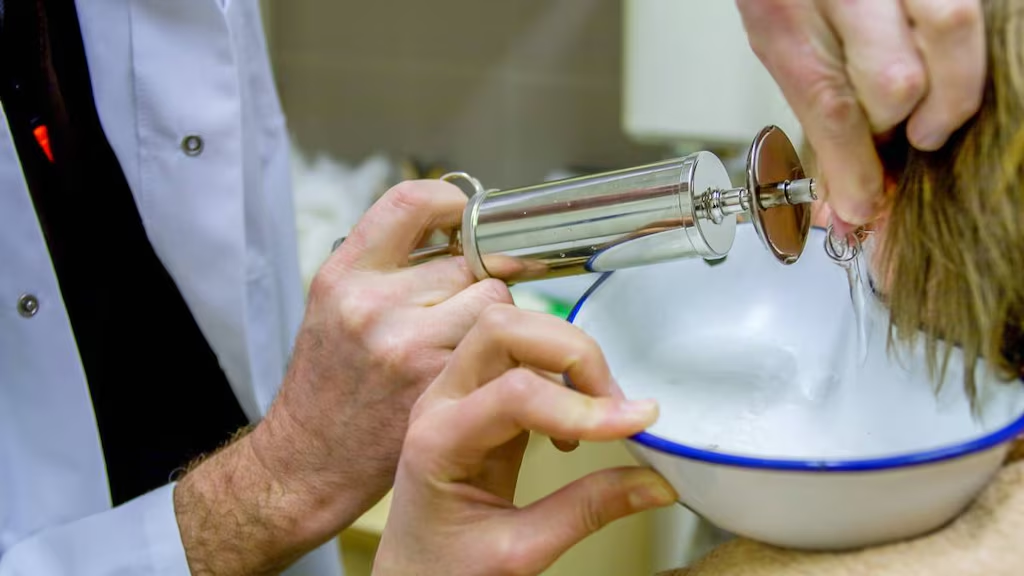

10:When to See a Doctor?
While mild swelling of the ear canal may improve with home care, it is important to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. See a doctor immediately if you experience severe or increasing pain, as this may indicate an infection that requires prescription treatment.Other warning signs include fever, persistent discharge, foul odor, or blood from the ear, which can signal bacterial or fungal infection. Significant hearing loss or a feeling of fullness that does not improve is another reason to consult a healthcare professional.
11:Chronic or Recurring Swelling
If swelling follows trauma, insect bites, or insertion of foreign objects, prompt medical evaluation is necessary to prevent complications. Chronic or recurring ear canal swelling, often linked to skin conditions or allergies, also requires medical guidance for long-term management.Early intervention ensures proper treatment, reduces the risk of permanent damage, and promotes faster healing while relieving pain and discomfort.
12:Arrange a Medical Appointment
If your swollen ear canal does not improve with home care or you experience severe symptoms, scheduling an appointment with a healthcare professional is essential. You can start by contacting your primary care physician or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. When booking, mention your symptoms, duration of swelling, any pain, discharge, or hearing changes, and any home remedies you have tried.
During the appointment, the doctor will examine your ear, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include ear drops, medication, or safe cleaning procedures. Prompt scheduling ensures timely diagnosis, prevents complications, and provides relief from discomfort.
For convenience, many clinics offer online appointment booking or telehealth consultations, allowing you to discuss your condition before visiting in person. Keeping a record of previous ear problems or allergies can help the doctor provide faster and more accurate care.

Wrap up
A swollen ear canal is a common condition caused by infections, allergies, trauma, earwax buildup, or skin irritations. Symptoms include pain, redness, itching, a feeling of fullness, and sometimes muffled hearing or discharge. Mild cases may improve with home care, such as keeping the ear clean and dry, using warm compresses, and avoiding inserting objects into the ear. However, persistent, severe, or recurring swelling requires medical attention. Doctors may prescribe antibiotic or antifungal drops, pain relievers, or perform safe cleaning procedures depending on the cause. Early diagnosis and treatment prevent complications, restore hearing, and reduce discomfort.
Frequently Asked Queries
1. What causes an ear canal?
An ear canal can result from infections, allergies, trauma, earwax buildup, or skin irritations. Moisture and foreign objects can also trigger inflammation.
2. Can a ear canal heal on its own?
Mild swelling from minor irritation or temporary moisture may heal naturally with proper ear care. Persistent or severe cases require medical treatment.
3. How can I reduce swelling at home?
Keep the ear dry, avoid inserting objects, use warm compresses and take over the counter pain relief. If symptoms worsen, consult a doctor.
4. When should I see a doctor?
Seek medical attention if swelling is severe, persistent, accompanied by pain, discharge, fever, hearing loss, or follows trauma or foreign object insertion.
5. What treatments do doctors recommend?
Depending on the cause, doctors may prescribe antibiotic or antifungal ear drops, corticosteroids, pain relievers, or safely clean the ear canal to reduce swelling.